
avenger
Redefine vector-borne diseases
Ancient yet persistently threaten human health worldwide

Every year, mosquito-borne diseases
There are many vector-borne diseases, but mosquito-borne diseases are the most significant and have the highest infection rates.
Female mosquitoes spread viruses by biting infected people and then biting others. Mosquitoes do not carry viruses naturally; they only get them from infected humans. Only female mosquitoes can transmit these diseases because only they bite humans.
Female mosquitoes spread viruses by biting infected people and then biting others. Mosquitoes do not carry viruses naturally; they only get them from infected humans. Only female mosquitoes can transmit these diseases because only they bite humans.
Infected
0
million people
Killed
0
million people
Reported Case
0
countries & territories
Epidemiological Updates: Ancient disease, resurgence
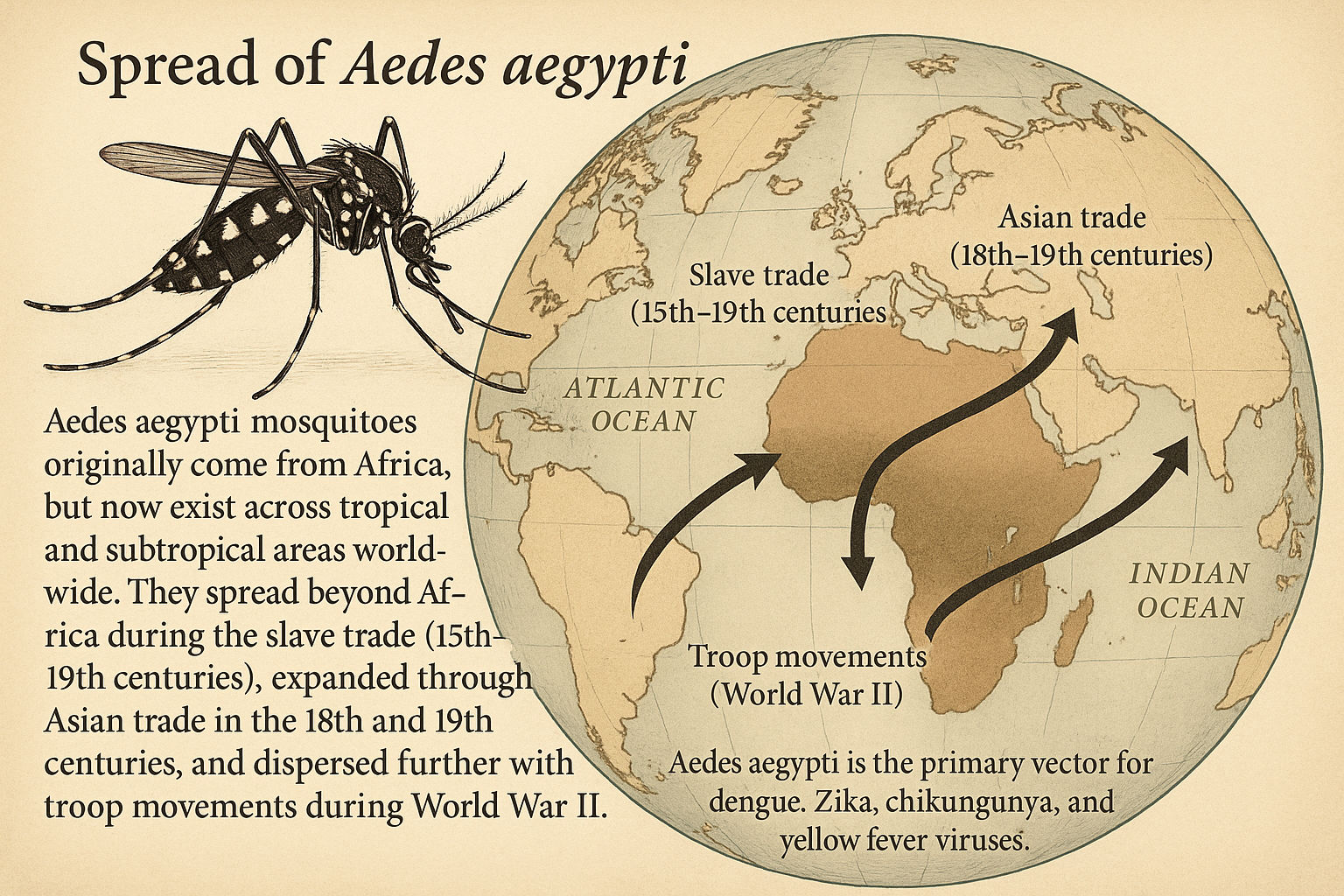
Aedes aegypti is the primary vector for dengue, Zika, chikungunya, and yellow fever viruses.
They originally come from Africa but now exist across tropical and subtropical areas worldwide. They spread beyond Africa during 15th–19th centuries, expanded through Asian trade in the 18th and 19th centuries, and dispersed further with troop movements during World War II.
They originally come from Africa but now exist across tropical and subtropical areas worldwide. They spread beyond Africa during 15th–19th centuries, expanded through Asian trade in the 18th and 19th centuries, and dispersed further with troop movements during World War II.
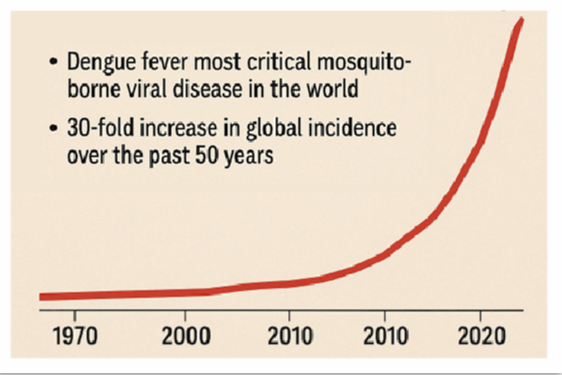
Mosquito-borne diseases are affecting more people than ever. Recent population growth, urbanization, increased international travel, and climate change have all helped Aedes aegypti mosquitoes spread further. As a result, more people are suffering from mosquito-borne illnesses.
According to the World Health Organization, dengue fever is now the most important and fastest-spreading mosquito-borne viral disease globally, with cases increasing 30-fold in the past 50 years.
According to the World Health Organization, dengue fever is now the most important and fastest-spreading mosquito-borne viral disease globally, with cases increasing 30-fold in the past 50 years.
Global dengue surveillance
Chikungunya outbreak in 2025, from Western to Easten
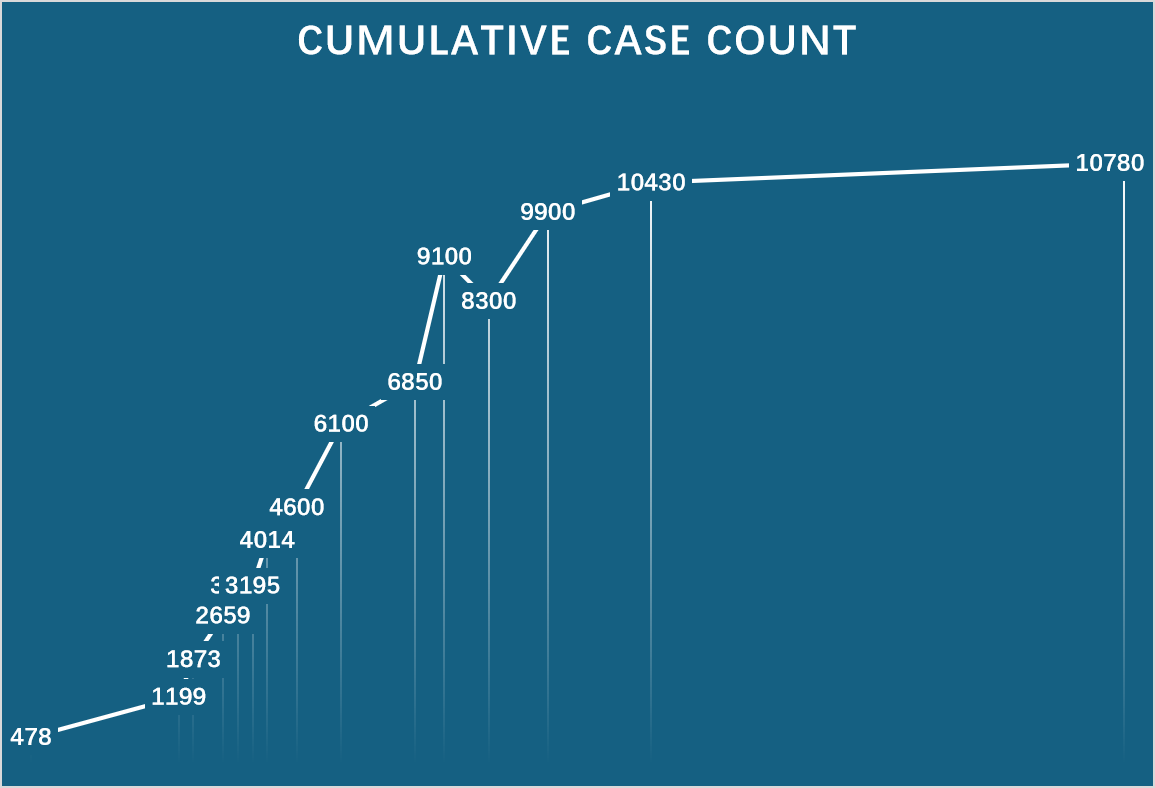
Cumulative case in 2025, Foshan Guangdong